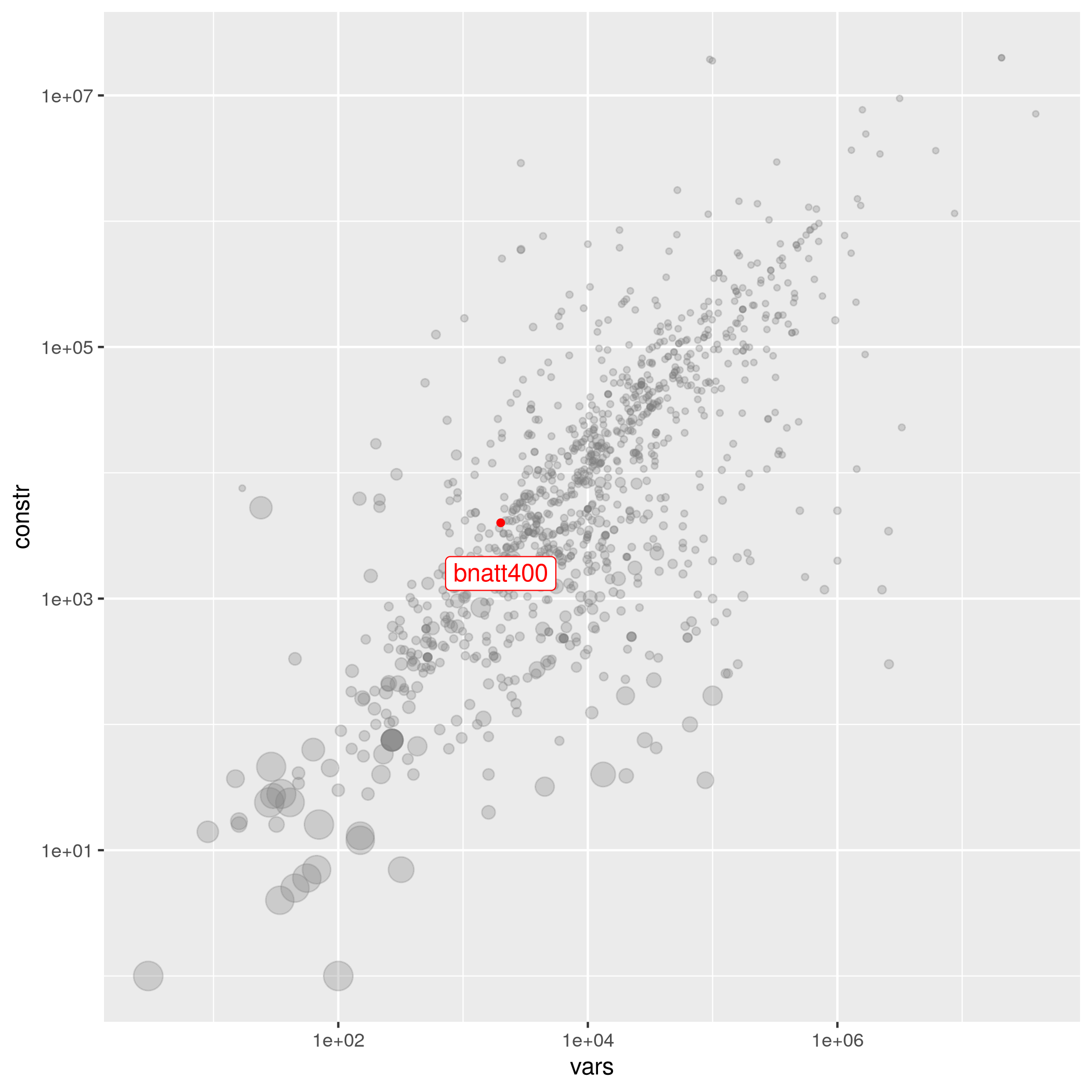
bnatt400
benchmark binary benchmark_suitable precedence set_covering invariant_knapsack binpacking knapsack
| Submitter | Variables | Constraints | Density | Status | Group | Objective | MPS File |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tatsuya Akutsu | 3600 | 5614 | 1.07361e-03 | easy | bnatt | 1 | bnatt400.mps.gz |
Model to identify a singleton attractor in a Boolean network, applications in computational systems biology. Solved by SCIP 3.0 with SoPlex 1.7.0 in half an hour. A Intel Core2 Extreme CPU X9659 @3.00GHz was used. Imported from MIPLIB2010.
Instance Statistics
Detailed explanation of the following tables can be found here.
| Original | Presolved | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | 3600 | 2003 |
| Constraints | 5614 | 4006 |
| Binaries | 3600 | 2003 |
| Integers | 0 | 0 |
| Continuous | 0 | 0 |
| Implicit Integers | 0 | 0 |
| Fixed Variables | 0 | 0 |
| Nonzero Density | 0.00107361 | 0.00209621 |
| Nonzeroes | 21698 | 16820 |
| Original | Presolved | |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 5614 | 4006 |
| Empty | 0 | 0 |
| Free | 0 | 0 |
| Singleton | 1586 | 0 |
| Aggregations | 0 | 0 |
| Precedence | 0 | 32 |
| Variable Bound | 0 | 0 |
| Set Partitioning | 0 | 0 |
| Set Packing | 0 | 0 |
| Set Covering | 1614 | 209 |
| Cardinality | 0 | 0 |
| Invariant Knapsack | 400 | 1778 |
| Equation Knapsack | 0 | 0 |
| Bin Packing | 0 | 383 |
| Knapsack | 0 | 1604 |
| Integer Knapsack | 0 | 0 |
| Mixed Binary | 2014 | 0 |
| General Linear | 0 | 0 |
| Indicator | 0 | 0 |
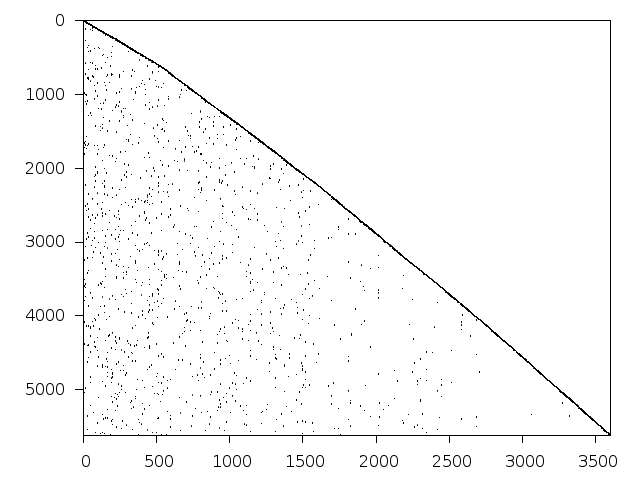
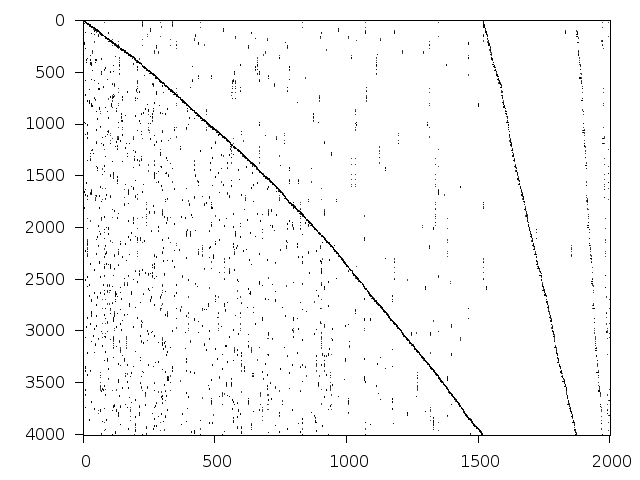
Structure
Available nonzero structure and decomposition information. Further information can be found here.

Decomposed structure of original problem (dec-file)
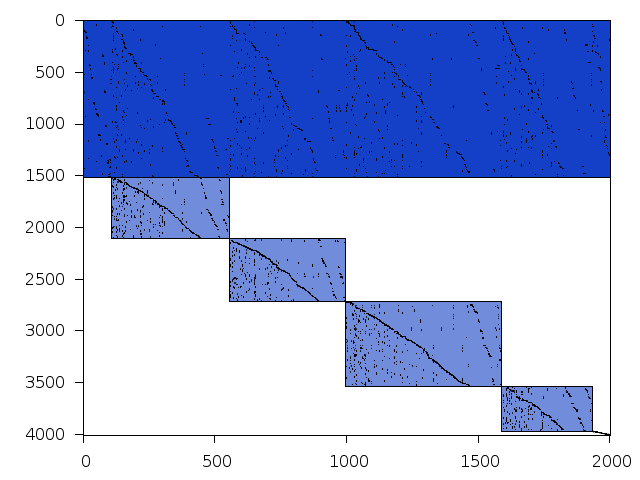
Decomposed structure after trivial presolving (dec-file)
| value | min | median | mean | max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Components | 2.482874 | ||||
| Constraint % | 0.0499251 | 0.0520671 | 0.0499251 | 0.249626 | |
| Variable % | 0.0998502 | 0.2703860 | 0.2496260 | 0.748877 | |
| Score | 0.157314 |
Best Known Solution(s)
Find solutions below. Download the archive containing all solutions from the Download page.
| ID | Objective | Exact | Int. Viol | Cons. Viol | Obj. Viol | Submitter | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 2018-10-11 | Solution imported from MIPLIB2010. |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 2018-10-11 | Solution found during MIPLIB2017 problem selection. |
Similar instances in collection
The following instances are most similar to bnatt400 in the collection. This similarity analysis is based on 100 scaled instance features describing properties of the variables, objective function, bounds, constraints, and right hand sides.
| Instance | Status | Variables | Binaries | Integers | Continuous | Constraints | Nonz. | Submitter | Group | Objective | Tags |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bnatt500 | easy | 4500 | 4500 | 0 | 0 | 7029 | 27203 | Tatsuya Akutsu | bnatt | Infeasible | benchmark infeasible binary benchmark_suitable precedence set_covering invariant_knapsack binpacking knapsack |
| s1234 | hard | 2945 | 2945 | 0 | 0 | 8418 | 44641 | Siwei Sun | SiweiSun | 29 | binary precedence set_covering invariant_knapsack binpacking knapsack |
| neos-5178119-nalagi | easy | 4167 | 4068 | 0 | 99 | 6921 | 74476 | Jeff Linderoth | neos-pseudoapplication-62 | 22.73999999763 | benchmark_suitable precedence set_partitioning set_packing set_covering cardinality invariant_knapsack knapsack mixed_binary general_linear |
| supportcase3 | easy | 4191 | 4191 | 0 | 0 | 12702 | 53470 | Michael Winkler | – | 0 | binary feasibility aggregations precedence variable_bound invariant_knapsack knapsack mixed_binary |
| circ10-3 | open | 2700 | 2700 | 0 | 0 | 42620 | 307320 | M. Winkler | – | 280* | binary decomposition precedence variable_bound set_partitioning set_packing invariant_knapsack knapsack mixed_binary |
Reference
@inproceedings{AkutsuHayashidaTamura2009,
author = {T. Akutsu and M. Hayashida and T. Tamura},
booktitle = {Proceedings of The combined 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and
Control and 28th Chinese Control Conference},
title = {Integer programming-based methods for attractor detection and control
of {B}oolean networks},
year = {2009}
}Last Update 2024 by Julian Manns
generated with R Markdown
© by Zuse Institute Berlin (ZIB)
Imprint