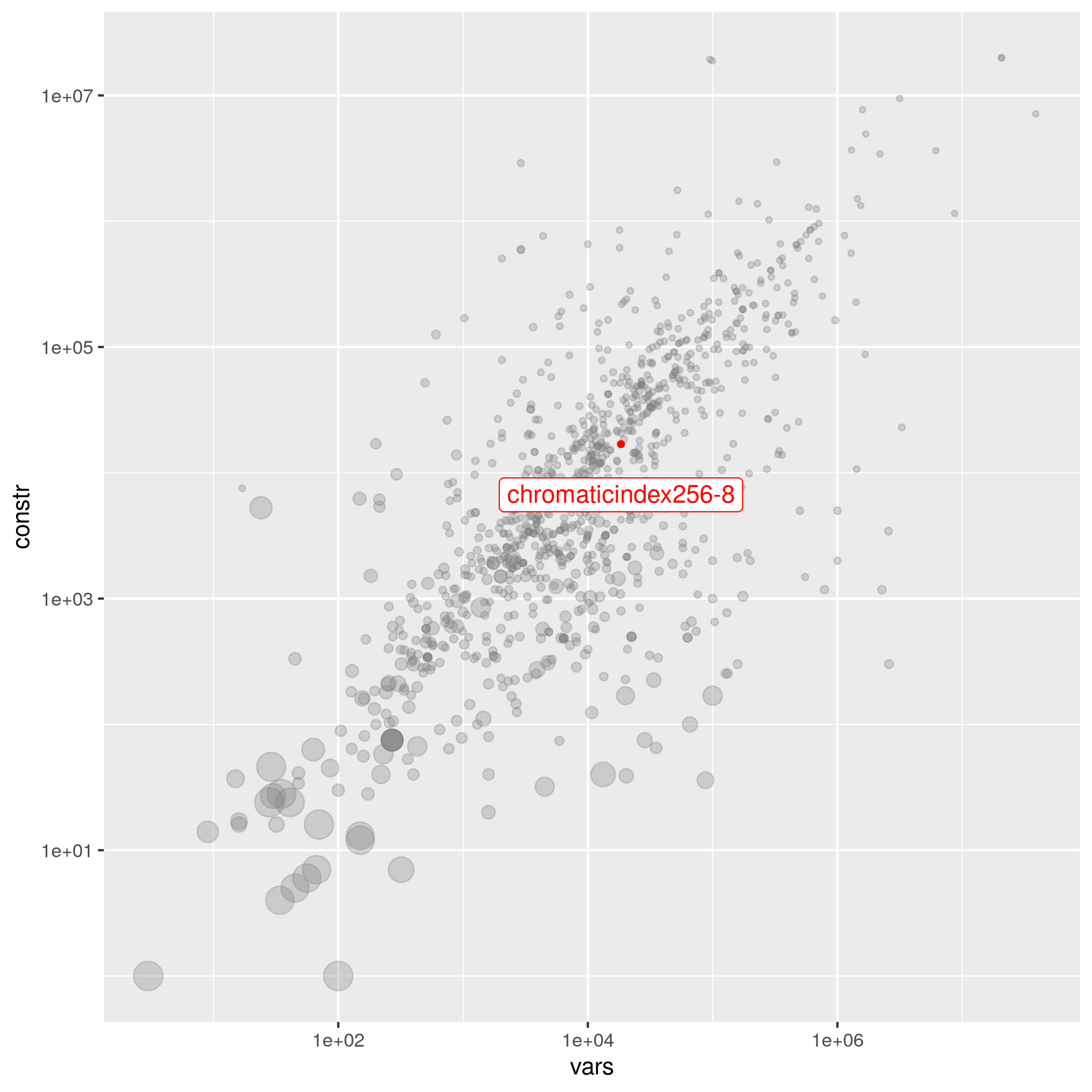
chromaticindex256-8
binary benchmark_suitable set_partitioning set_packing
| Submitter | Variables | Constraints | Density | Status | Group | Objective | MPS File |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pierre Le Bodic | 18432 | 16895 | 2.16988e-04 | easy | chromaticindex | 4 | chromaticindex256-8.mps.gz |
Simple edge-coloring model on chains of Petersen-like subgraphs, designed to fool MIP solvers into producing very large Branch-and-Bound trees.
Instance Statistics
Detailed explanation of the following tables can be found here.
| Original | Presolved | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | 18432 | 18432 |
| Constraints | 16895 | 16895 |
| Binaries | 18432 | 18432 |
| Integers | 0 | 0 |
| Continuous | 0 | 0 |
| Implicit Integers | 0 | 0 |
| Fixed Variables | 0 | 0 |
| Nonzero Density | 0.000216988 | 0.000216988 |
| Nonzeroes | 67572 | 67572 |
| Original | Presolved | |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 16895 | 16895 |
| Empty | 0 | 0 |
| Free | 0 | 0 |
| Singleton | 0 | 0 |
| Aggregations | 0 | 0 |
| Precedence | 0 | 0 |
| Variable Bound | 0 | 0 |
| Set Partitioning | 4607 | 4607 |
| Set Packing | 12288 | 12288 |
| Set Covering | 0 | 0 |
| Cardinality | 0 | 0 |
| Invariant Knapsack | 0 | 0 |
| Equation Knapsack | 0 | 0 |
| Bin Packing | 0 | 0 |
| Knapsack | 0 | 0 |
| Integer Knapsack | 0 | 0 |
| Mixed Binary | 0 | 0 |
| General Linear | 0 | 0 |
| Indicator | 0 | 0 |
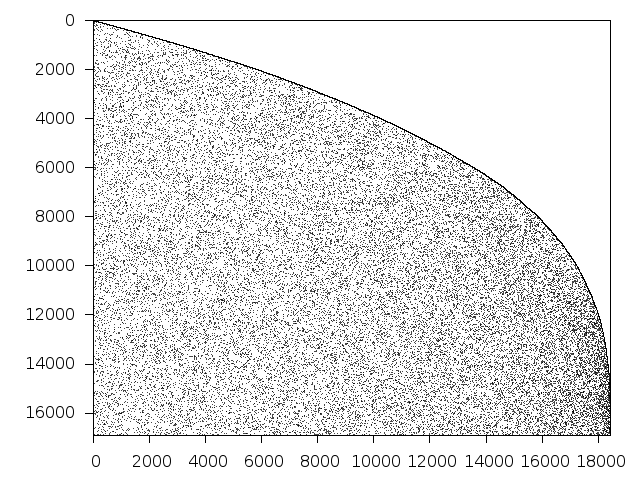
Structure
Available nonzero structure and decomposition information. Further information can be found here.
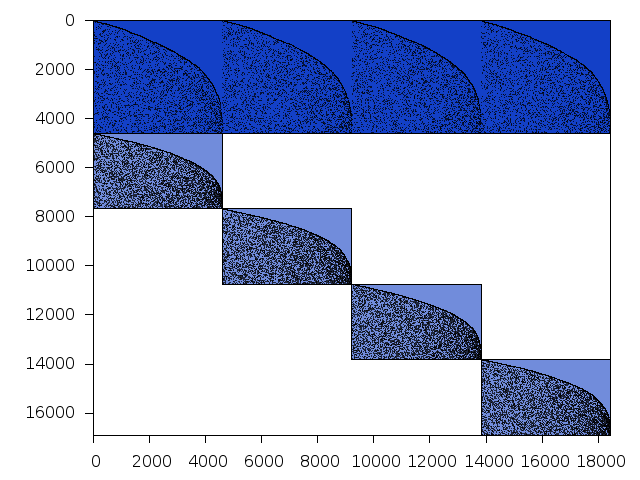
Decomposed structure of original problem (dec-file)
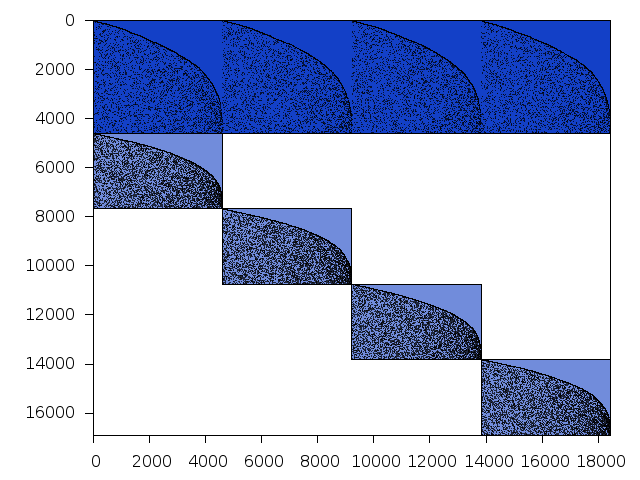
Decomposed structure after trivial presolving (dec-file)
| value | min | median | mean | max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Components | 0.698970 | ||||
| Constraint % | 18.1829 | 18.1829 | 18.1829 | 18.1829 | |
| Variable % | 25.0000 | 25.0000 | 25.0000 | 25.0000 | |
| Score | 0.545487 |
Best Known Solution(s)
Find solutions below. Download the archive containing all solutions from the Download page.
| ID | Objective | Exact | Int. Viol | Cons. Viol | Obj. Viol | Submitter | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 2018-10-13 | Solution found during MIPLIB2017 problem selection. |
Similar instances in collection
The following instances are most similar to chromaticindex256-8 in the collection. This similarity analysis is based on 100 scaled instance features describing properties of the variables, objective function, bounds, constraints, and right hand sides.
| Instance | Status | Variables | Binaries | Integers | Continuous | Constraints | Nonz. | Submitter | Group | Objective | Tags |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chromaticindex128-5 | easy | 9216 | 9216 | 0 | 0 | 8447 | 33780 | Pierre Le Bodic | chromaticindex | 4 | binary benchmark_suitable set_partitioning set_packing |
| chromaticindex512-7 | easy | 36864 | 36864 | 0 | 0 | 33791 | 135156 | Pierre Le Bodic | chromaticindex | 4 | benchmark binary benchmark_suitable set_partitioning set_packing |
| chromaticindex1024-7 | easy | 73728 | 73728 | 0 | 0 | 67583 | 270324 | Pierre Le Bodic | chromaticindex | 4 | benchmark binary benchmark_suitable set_partitioning set_packing |
| chromaticindex32-8 | easy | 2304 | 2304 | 0 | 0 | 2111 | 8436 | Pierre Le Bodic | chromaticindex | 4 | binary benchmark_suitable set_partitioning set_packing |
| netdiversion | easy | 129180 | 129180 | 0 | 0 | 119589 | 615282 | Chris Cullenbine | – | 242 | benchmark binary benchmark_suitable precedence variable_bound set_partitioning set_packing cardinality invariant_knapsack |
Reference
@article{lebodicnemhauser2015,
title = "How important are branching decisions: Fooling \{MIP\} solvers ",
journal = "Operations Research Letters ",
volume = "43",
number = "3",
pages = "273 - 278",
year = "2015",
note = "",
issn = "0167-6377",
doi = "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.orl.2015.03.003",
url = "//www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167637715000413",
author = "Pierre Le Bodic and George L. Nemhauser",
keywords = "Mixed integer programming solvers",
keywords = "Branch and bound",
keywords = "Tree size",
keywords = "Edge coloring",
keywords = "Chromatic index "
}Last Update Mar 04, 2024 by Julian Manns
generated with R Markdown
© 2023 by Zuse Institute Berlin (ZIB)
Imprint