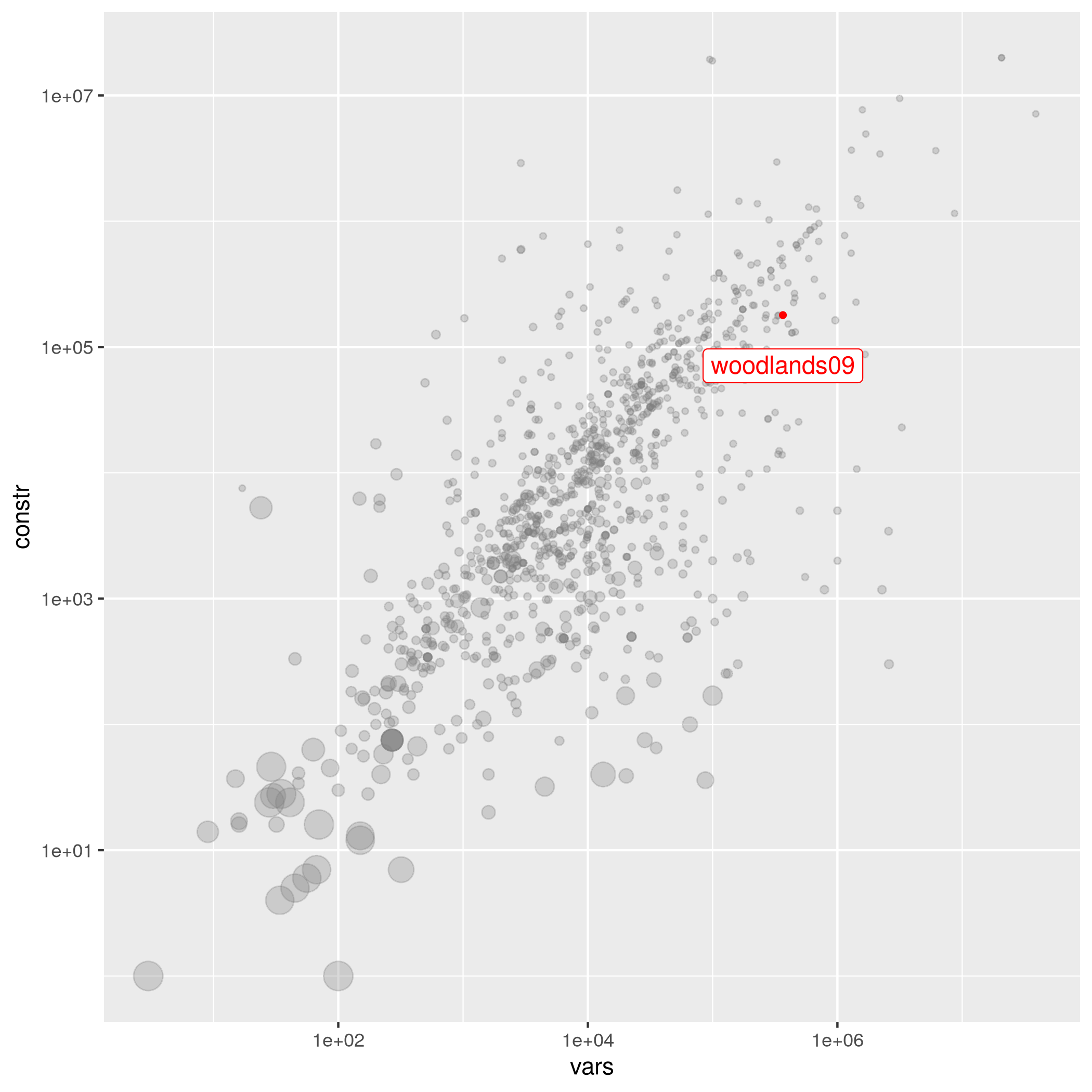
woodlands09
aggregations variable_bound set_partitioning set_packing set_covering cardinality invariant_knapsack equation_knapsack general_linear
| Submitter | Variables | Constraints | Density | Status | Group | Objective | MPS File |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| George Fonseca | 382147 | 194599 | 3.55811e-05 | hard | timetabling | 0 | woodlands09.mps.gz |
Educational timetabling problems from several real schools/universities around the world. These instances were originally expressed in the xhstt file format [1] and formulated as Integer Programming models as described at [2].
[1] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0377221717302242 [2] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10479-011-1012-2 Reported to be solved after 243275 seconds with ParaSCIP using 72 cores.
Instance Statistics
Detailed explanation of the following tables can be found here.
| Original | Presolved | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | 382147 | 365837 |
| Constraints | 194599 | 179345 |
| Binaries | 382119 | 365809 |
| Integers | 28 | 28 |
| Continuous | 0 | 0 |
| Implicit Integers | 0 | 4 |
| Fixed Variables | 0 | 0 |
| Nonzero Density | 3.55811e-05 | 3.69208e-05 |
| Nonzeroes | 2646000 | 2422410 |
| Original | Presolved | |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 194599 | 179345 |
| Empty | 0 | 0 |
| Free | 0 | 0 |
| Singleton | 3877 | 0 |
| Aggregations | 58718 | 56236 |
| Precedence | 0 | 0 |
| Variable Bound | 6720 | 3840 |
| Set Partitioning | 9030 | 9119 |
| Set Packing | 8787 | 8787 |
| Set Covering | 2943 | 1289 |
| Cardinality | 3039 | 1480 |
| Invariant Knapsack | 6102 | 6088 |
| Equation Knapsack | 95376 | 92499 |
| Bin Packing | 0 | 0 |
| Knapsack | 0 | 0 |
| Integer Knapsack | 0 | 0 |
| Mixed Binary | 0 | 0 |
| General Linear | 7 | 7 |
| Indicator | 0 | 0 |
Structure
Available nonzero structure and decomposition information. Further information can be found here.

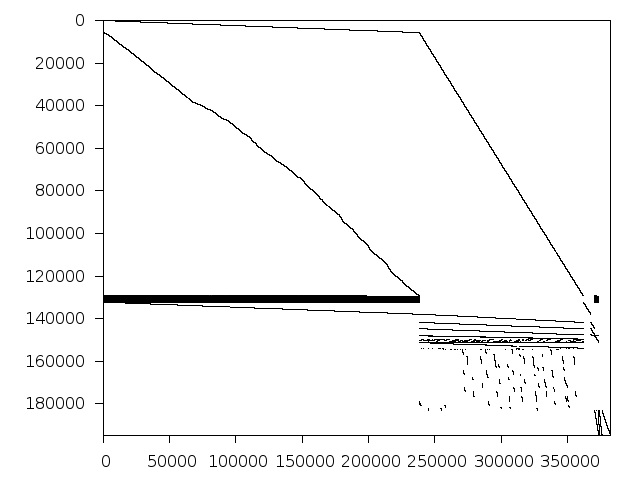
Decomposed structure of original problem (dec-file)
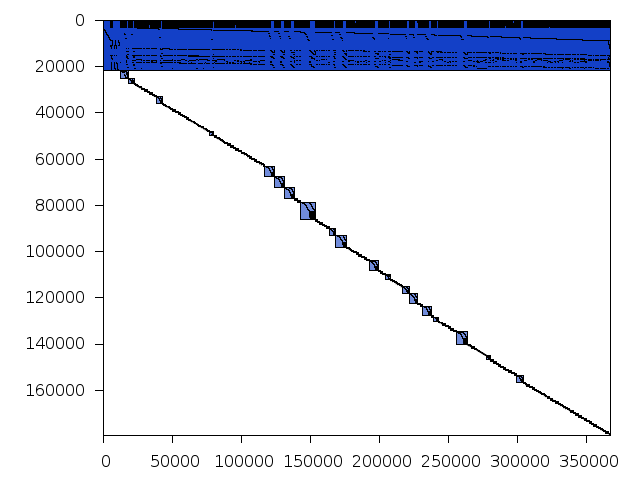
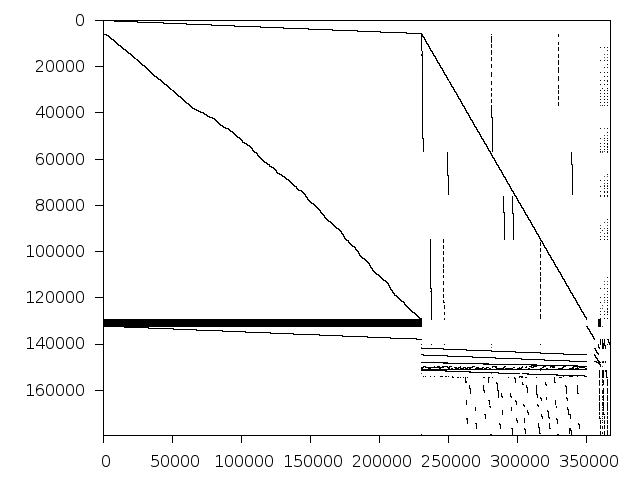
Decomposed structure after trivial presolving (dec-file)
| value | min | median | mean | max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Components | |||||
| Constraint % | |||||
| Variable % | |||||
| Score |
Best Known Solution(s)
Find solutions below. Download the archive containing all solutions from the Download page.
| ID | Objective | Exact | Int. Viol | Cons. Viol | Obj. Viol | Submitter | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Yuji Shinano | 2018-11-01 | Found with ParaSCIP using 72 cores |
Similar instances in collection
The following instances are most similar to woodlands09 in the collection. This similarity analysis is based on 100 scaled instance features describing properties of the variables, objective function, bounds, constraints, and right hand sides.
Reference
@article{FONSECA201728,
title = "Integer programming techniques for educational timetabling",
journal = "European Journal of Operational Research",
volume = "262",
number = "1",
pages = "28 - 39",
year = "2017",
note = "",
issn = "0377-2217",
doi = "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2017.03.020",
url = "http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0377221717302242",
author = "George H.G. Fonseca and Haroldo G. Santos and Eduardo G. Carrano and Thomas J.R. Stidsen",
keywords = "Timetabling",
keywords = "Integer Programming",
keywords = "Formulation"
}Last Update 2024 by Julian Manns
generated with R Markdown
© by Zuse Institute Berlin (ZIB)
Imprint